 +
+  = m
= m , with
, with  the weight of the pendulum and m its
mass,
the weight of the pendulum and m its
mass,  the tension in rod, and
the tension in rod, and 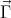 the centripetal acceleration (see Fig. 1).
the centripetal acceleration (see Fig. 1).
Considering the Earth as an inertial frame of reference, we can apply Newton’s second
law to the pendulum:  +
+  = m
= m , with
, with  the weight of the pendulum and m its
mass,
the weight of the pendulum and m its
mass,  the tension in rod, and
the tension in rod, and 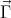 the centripetal acceleration (see Fig. 1).
the centripetal acceleration (see Fig. 1).
We thus deduce :
and consequently
 | (3) |
If we consider l sin θ as negligible compared to R, we get the 0th-order solution:
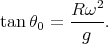 | (4) |